08-24-2021
08-24-2021
From public finance to defense to healthcare, enterprises across all sectors are adopting cloud-first and hybrid models to rapidly deliver cutting-edge solutions for today’s most pressing problems. Cloud computing allows users to scale services to fit their needs, develop and deploy quickly, and access services anytime anywhere. However, the benefits of cloud services can be undermined when an enterprise has its users connect to the cloud via the public Internet, which can create potential data breaches, reduce network performance, and make security configurations difficult to manage. In this article, we’ll walk through how an Internet-isolated architecture can avoid these pitfalls and ensure the security of your cloud connections.
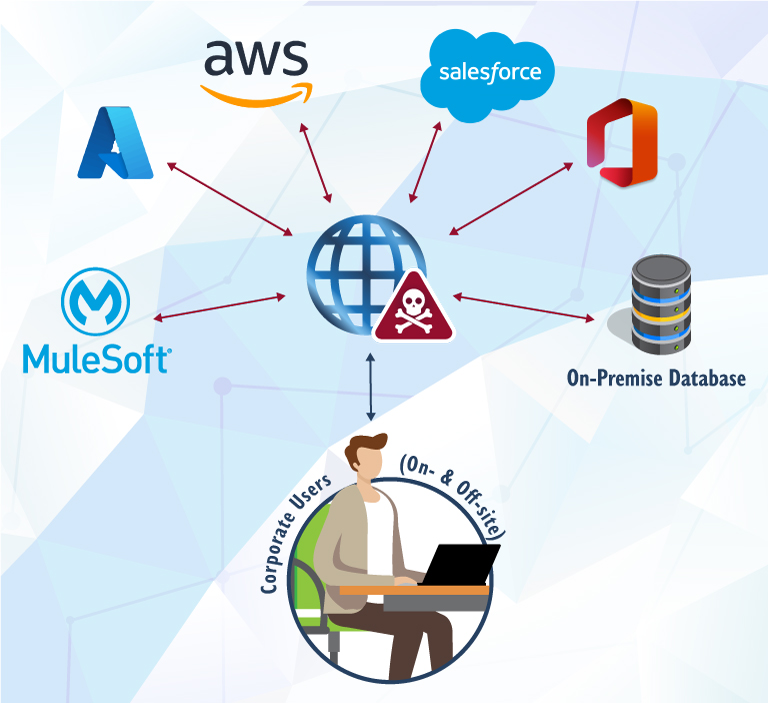
While connecting directly to an enterprise cloud environment via the Internet is simple and convenient, anything exposed to the public Internet is subject to attack by anyone anywhere. Security scanning tools often observe malicious bots probing ports for security vulnerabilities within hours of deploying something publicly. Exposed ports leave users and servers vulnerable to backdoor hacks, distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks, injection attacks, man-in-the-middle attacks, and data exposure due to lack of encryption. In short, accessing the cloud directly through the Internet, as depicted below, is risky business.
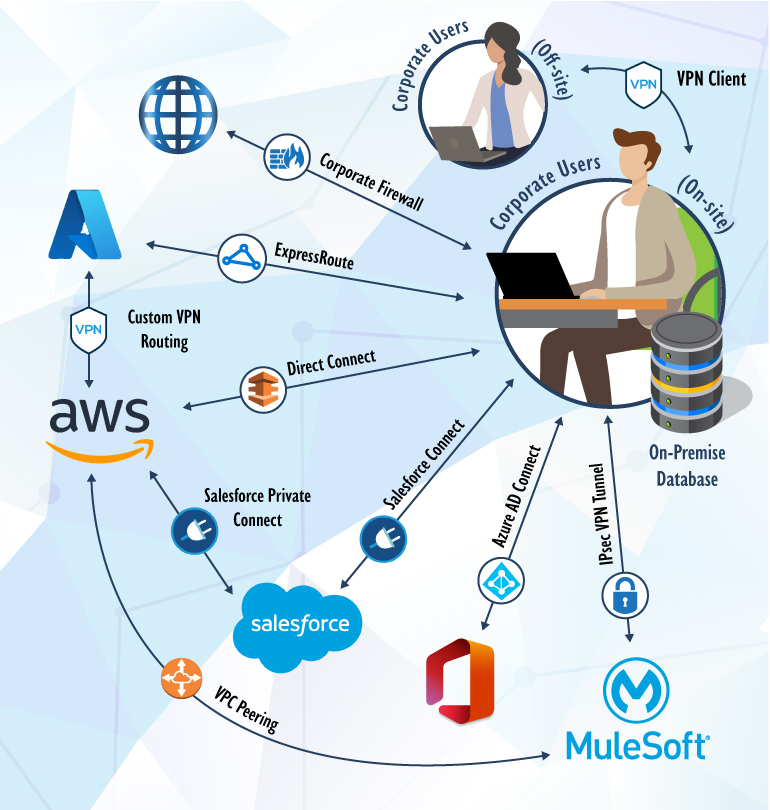
Considering these risks, we recommend designing a hybrid cloud architecture that only exposes cloud resources directly to the Internet when necessary, as is the case for public-facing websites and public application programming interfaces (APIs). In any case, firewalls, virtual private networks (VPNs), direct cloud connections, and virtual private cloud (VPC) peering are key to securing connections to your cloud resources, minimizing the attack surface, and optimizing network speeds. Below is an example showing how you can use these four tools to build a secure hybrid cloud environment.
Firewalls are the first line of defense when it comes to securing, monitoring, and regulating corporate network connections and communications. A corporate firewall gives your business full control over who and what goes in and out of the network by restricting port exposure and limiting access to a specified range of IP addresses, preventing unauthorized users from accessing your corporate network from the wider Internet while protecting public-facing assets.
VPNs are another must-have for any secure enterprise network and cloud environment, especially when your workforce is remote. With a VPN client, offices and remote users can securely connect to enterprise resources over the Internet, encrypting traffic between users and servers while preventing attackers from identifying what cloud services you’re using. IP Security (IPsec) VPNs can also provide a layer of security between an office and a cloud service by encrypting data in transit and the endpoints themselves via tunnel mode, preventing attackers from locating your network endpoints.
Direct cloud connection solutions like ExpressRoute, Salesforce Connect, AWS Direct Connect, and Azure AD Connect make it easy to establish a dedicated network connection from your premises to different cloud environments. With direct connections, you establish a private connection between the cloud service provider and your data center, office, or colocation environment. By leveraging plug-and-play direct connection services, enterprises can increase bandwidth throughput, lower network costs, secure data in transit via encryption, and provide a more consistent network experience than Internet-based connections.
VPC peering is a great way to isolate and securely route traffic between two VPC instances hosted either (1) with the same AWS account or (2) across separately owned AWS accounts. This will enable resources to communicate using private IP addresses rather than public (vulnerable) IPs. Some PaaS/SaaS vendors like Mulesoft leverage common cloud hosting providers like AWS on the backend of their tools, which allows you to peer their individual networks. Enterprises can leverage the existing infrastructure of an AWS VPC to establish peer connections that keep traffic securely within a single cloud provider network, while reducing network transit costs and improving network latency.
As more organizations move to the cloud, CIOs and IT administrators need a strategy for secure cloud access that accounts for the myriad threats in today’s cyber landscape. Designing an Internet-isolated cloud environment is one of the most effective ways to hedge against cyberattacks and secure assets, ensuring your enterprise can realize the full value of cloud computing and gain a competitive edge.